The buildup of excess fluid in the body’s tissues, which leads to swelling, is a condition known as edema. While it can affect anyone, certain individuals are more prone to developing edema due to specific health conditions, lifestyle factors, or genetic predispositions. Understanding the risk factors of edema and how to manage it can help individuals maintain better overall health and prevent complications.
What Is Edema?
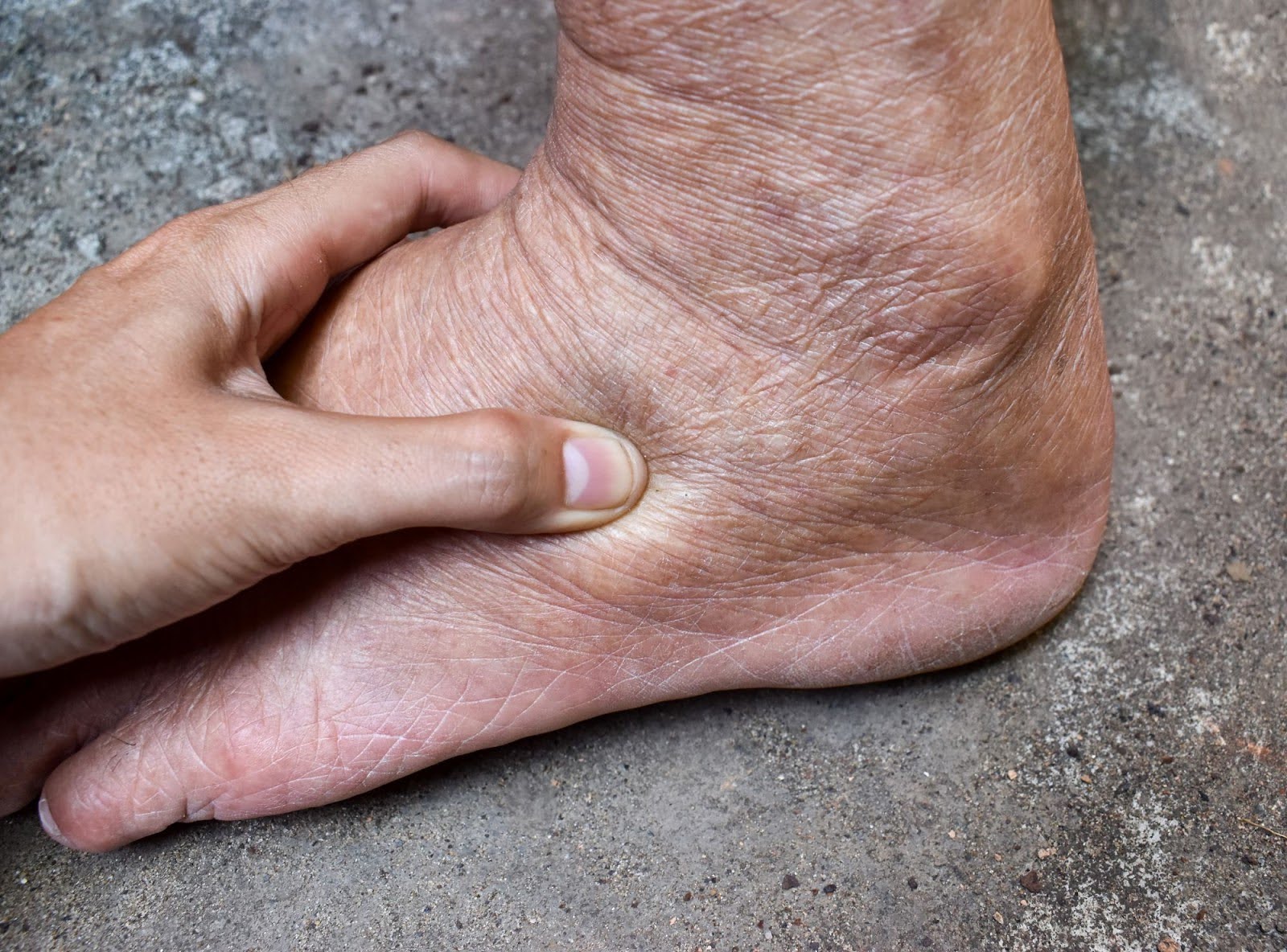
Edema occurs when fluid accumulates in the free spaces of the body’s tissues, most commonly in the legs, feet, ankles, hands, and sometimes even the lungs. The swelling can range from mild to severe and may be temporary or chronic, depending on the underlying cause. It can fluctuate during the day and with activity, or it can be more sustained.
Understanding the Types of Edema
Edema is a general term that covers a variety of subtypes of fluid retention that can occur in the body. It’s important to note that each form of edema has drastically different causes and implications for health, and each requires different treatments. Types of edema include:
- Peripheral Edema: One of the most visible types of edema, this leads to swelling in the legs, feet, or arms due to fluid retention. It is often caused by poor circulation or prolonged sitting/standing. Acute or recent injuries can also cause edema in the affected area for a short time.
- Lymphedema: This is when fluid retention happens due to a damaged or blocked lymphatic system. It is commonly seen after cancer treatments that disrupt local lymph nodes and channels, like a mastectomy or radiation.
- Pulmonary Edema: This is fluid accumulation in the lungs, which can be life-threatening and is often linked to heart conditions.
- Cerebral Edema: Also known as swelling in the brain, this is typically due to injury, infection, or a stroke. Like pulmonary edema, it is life-threatening.
Who Is at Risk for Edema?
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing edema due to various health conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors.
- Heart Disease and Circulatory Issues: Conditions such as congestive heart failure, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and chronic venous insufficiency can cause fluid to accumulate in the lower extremities. These conditions are risk factors of pulmonary edema.
- Kidney Disease: The kidneys play a vital role in fluid regulation, and any dysfunction can lead to water retention and swelling.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on blood vessels often result in mild to moderate swelling, particularly in the legs and feet.
- Medications: Some medications, such as steroids, calcium channel blockers, NSAIDs, and certain antidepressants, can contribute to fluid retention.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Sitting or standing for extended periods can cause fluid to pool in the legs and feet.
Managing and Reducing Edema to Regain Your Life
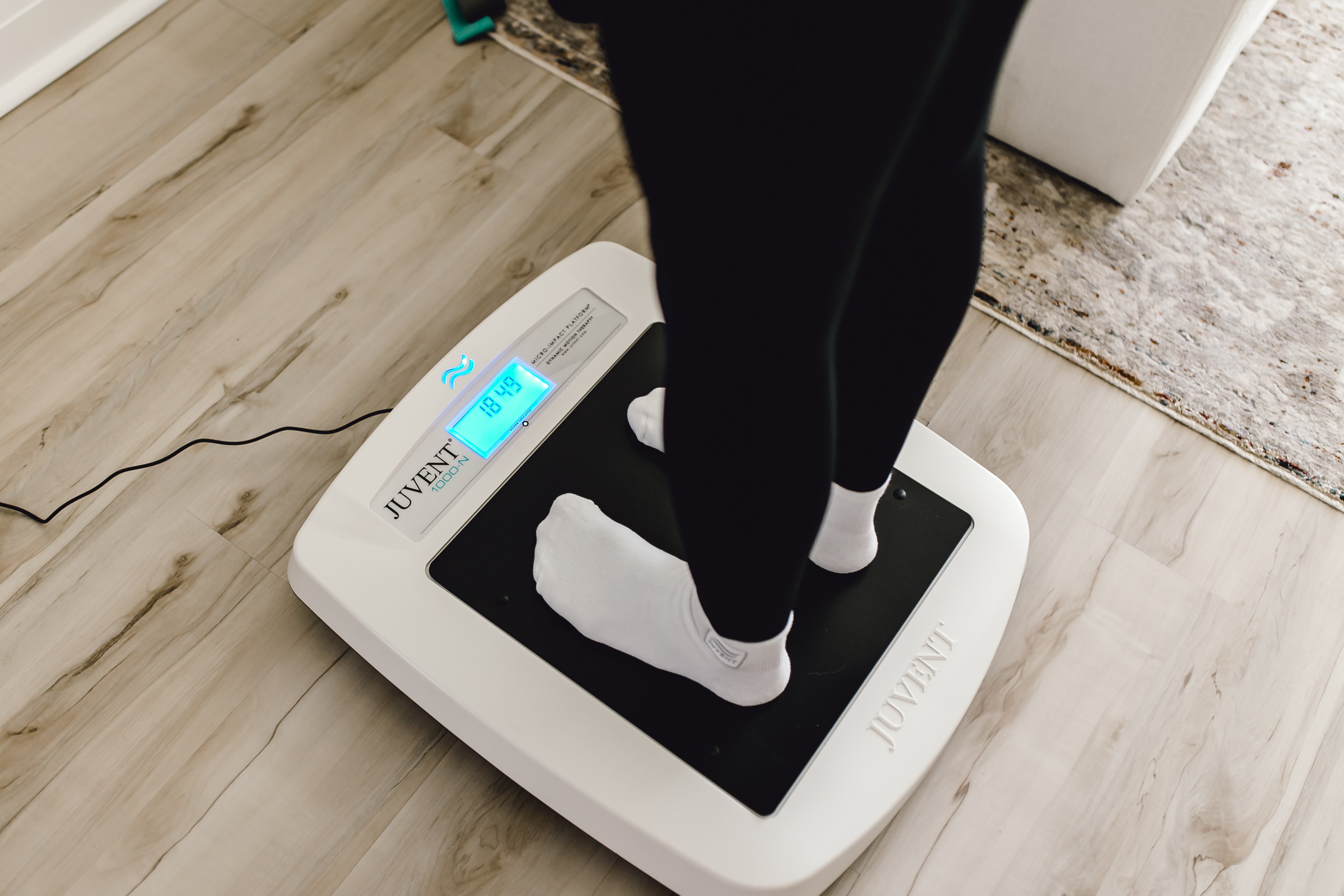
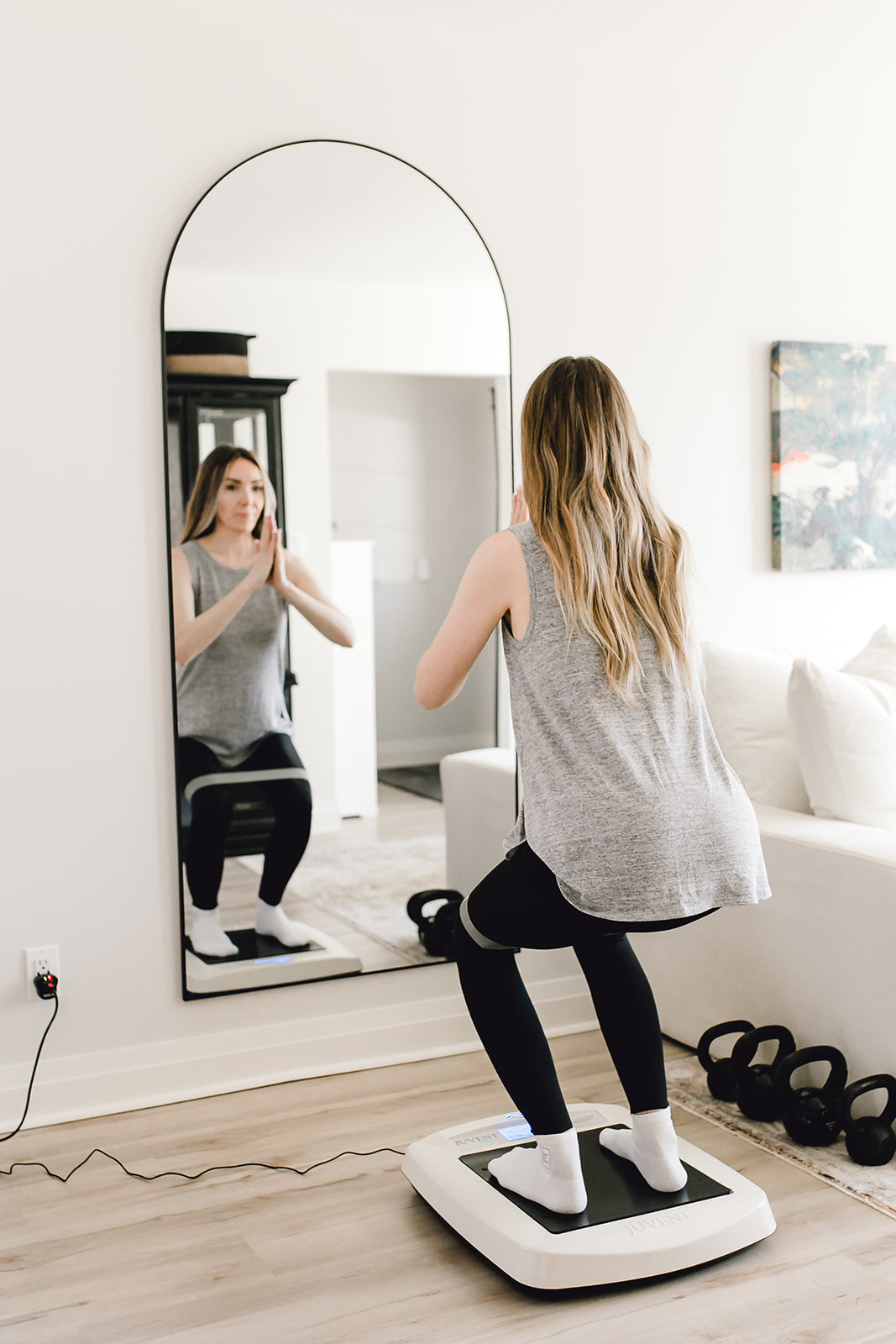
While edema can be uncomfortable and concerning, there are several effective ways to manage it and reduce swelling. Lifestyle modifications are a common first step, depending on your medical history. This includes a lower-sodium diet that helps prevent excess water retention. Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, and stretching, can promote circulation and fluid movement. When resting, raising your legs above heart level can help reduce swelling in the lower extremities. Wearing compression socks or sleeves can support circulation and reduce fluid buildup. Other convenient options include tools that stimulate circulation and activity, like the Juvent Micro-Impact Platform®. Through patented technology, the platform delivers low-magnitude mechanical stimulation that automatically calibrates to your body’s frequency to promote blood flow, lymphatic drainage, and overall joint health. It’s a valuable edema management strategy that is simple to use and doesn’t require leaving home.
Certain individuals may require more dedicated medical intervention for their edema. Doctors may prescribe diuretics to help the body eliminate excess fluid, but these should only be taken under medical supervision. Proper treatment of heart disease, kidney disease, or liver issues can help prevent edema from worsening. For lymphedema patients, specialized massage techniques can help move trapped fluid.
When to See a Doctor
There may come a point where it is essential to seek medical attention, including if the edema is sudden, severe, or painful. If you experience difficulty breathing or the swelling does not improve with self-care measures, you should see your healthcare provider. On the limbs, if there is skin discoloration or an open wound in the swollen area, it should also be checked by a professional.
Take Control of Your Edema
Understanding the many edema risk factors can help you take proactive steps to prevent and manage edema. As always, consulting a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. With their guidance, making lifestyle changes, addressing underlying health conditions, and utilizing supportive therapies like the Juvent Micro-Impact Platform, you may improve circulation, reduce swelling, and enhance your overall well-being.
FDA Disclosure
In the US, the Juvent device is considered investigational for the treatment of osteoporosis or improvement/maintenance of bone mineral density and our claims have not been reviewed or cleared by the FDA to treat any disease or condition. (2) Calculated over the 20+ year expected life of a Juvent. The JUVENT® Micro-Impact Platform® is Registered as a Class I medical device for exercise and rehabilitation. JUVENT products are covered by the following issued patents, pending patents and their foreign equivalents: 6,843,776 6,884,2277,094211 7,207,954 7,207,955 7,985,191 8,114,036 11/369,611 11/486,538. Juvent, Dynamic Motion Therapy, Micro-Impact Platform, and the symbol are Registered trademarks of Regenerative Technologies Corporation.



Share:
Understanding the Different Risks for Indoor and Outdoor Sports
Having Trouble Sleeping? Try These Six Things Before Bed